Comparison-based Algorithm: Decision Tree
- Relate the process of any comparison-based algorithm to a decision tree.
The operations of any comparison-based algorithm can be viewed as a tree of all possible comparison outcomes and resulting output. Such a tree is called a decision tree (or a comparison tree).
Recall we illustrated the operation of binary search as a decision tree:
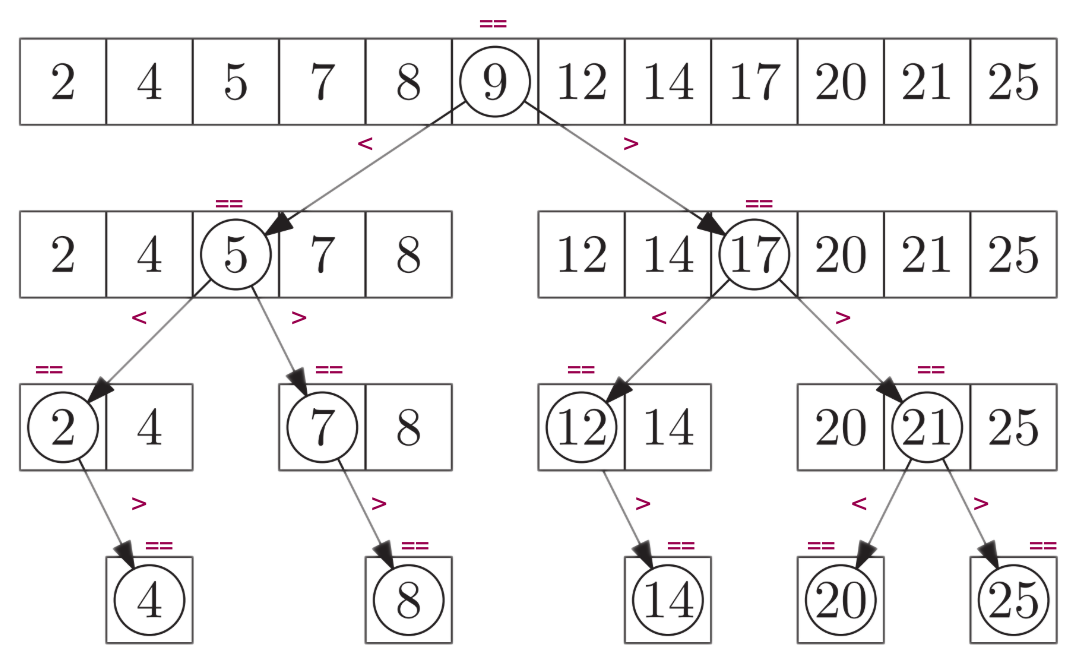
Explanation
Assume the target value is $x$; we start the search by comparing the value of $x$ to the value of the element in the middle of the sequence, $9$. If $x = 9$ then the search ends. Otherwise, there are two possible outcomes:
- $x>9$ in which case we will explore the right half of the sequence (the next comparison will be against $17$).
- $x<9$ in which case we will explore the left half of the sequence (the next comparison will be against $5$)
This process is repeated until the search succeeds or fails (no more values are left to compare).
A decision tree is a flowchart-like structure that models the comparisons made and their possible outcomes (consequences).