Graph Representation: Adjacency List
- Explain the adjacency list representation of a graph.
- Differentiate between adjacency and incidence list representations.
An adjacency list is a list of lists: each list corresponds to a vertex $u$ and contains a list of vertices adjacent to it.
Here is an example for an undirected graph:
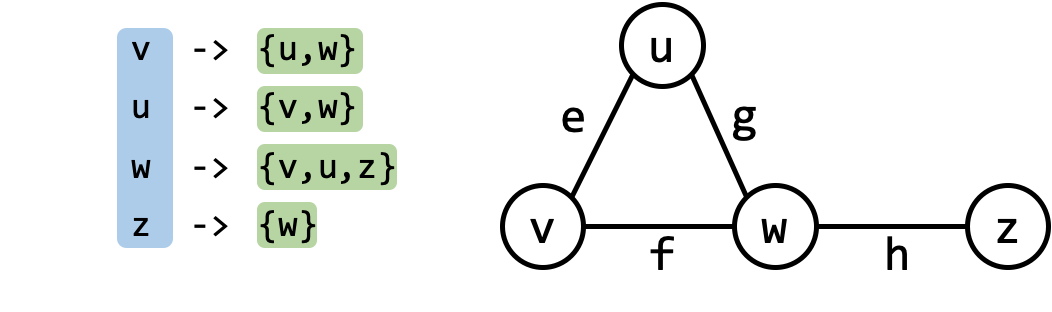
Here is an example for directed graph:
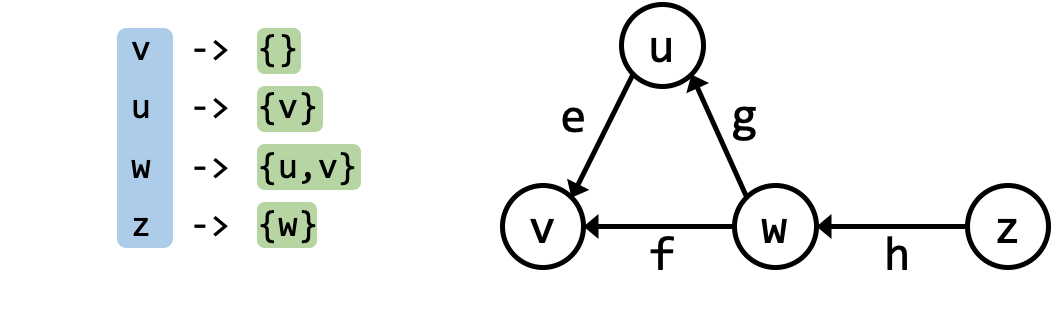
Incidence List
An incidence list is similar to an adjacency list except that each vertex $u$ is mapped to a list of edges $(u, v)$ incident to $u$.
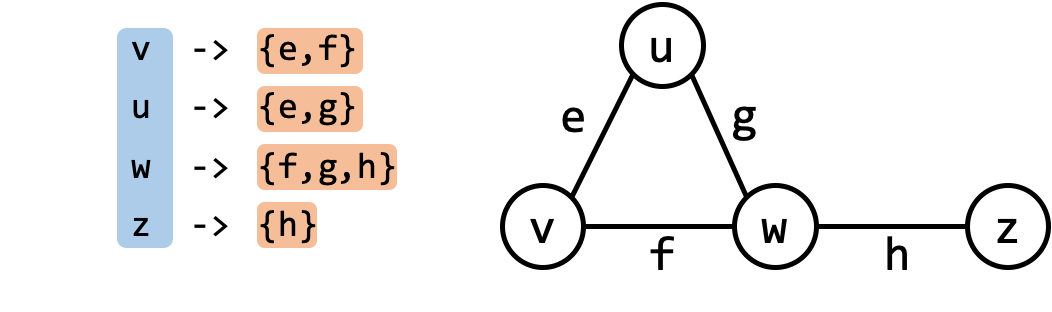
In many references, the adjacency list is defined as what I have described as an incidence list!
The space requirement for adjacency/incidence list representation is $\Omicron(N+M)$.
You need a list of vertices $\Omicron(N)$, and each vertex has a list of its adjacent vertices (or incident edges). The size of the list will be equal to the degree of that vertex. The total size is the sum of the degree of all vertices, which is $2M$. (See "degree sum formula" discussed earlier.)